October 23, 2025
Complete Guide to Federal Grant Compliance Rules
Federal grant compliance ensures public funds are used responsibly and transparently. For public safety agencies and municipalities, following these rules is critical to maintaining funding and eligibility for future grants. Non-compliance risks financial penalties and funding loss.
Key compliance areas include:
- Allowable Costs: Expenses must be necessary, reasonable, and documented. Examples include personnel costs and equipment tied to grant objectives. Unallowable costs include entertainment, alcohol, and lobbying.
- Procurement Standards: Rules vary by purchase amount. Larger purchases require competitive processes and documentation.
- Subrecipient Monitoring: Agencies must oversee partners to ensure they meet federal requirements.
- Audit and Reporting: Organizations spending $750,000+ in federal funds annually must comply with Single Audit requirements and maintain detailed financial and performance records.
New 2025 updates to federal regulations emphasize stricter reporting, cybersecurity, and subrecipient oversight. Tools like Grantwell simplify compliance with automated tracking, alerts, and audit preparation.
Take Action: Review your compliance processes, train staff, and consider technology solutions to streamline grant management.
Federal Grants Compliance and Audit Requirements: Best Practices and Watch-outs - Session 1
Core Federal Grant Compliance Requirements
Successfully managing federal grants requires public safety and municipal agencies to navigate four key areas. These pillars are essential for responsible grant management and ensuring continued funding eligibility.
Allowable vs. Unallowable Costs
Understanding which costs qualify as allowable is a cornerstone of compliance. The 2 CFR 200 Uniform Guidance serves as the rulebook, but its complexity can vary depending on the grant.
Allowable costs must meet specific criteria: they need to be necessary, reasonable, allocable, and thoroughly documented. For law enforcement agencies, this might include personnel costs tied to grant-funded efforts, project-related equipment, and training expenses directly tied to the grant’s objectives.
Some examples of allowable costs include:
- Overtime pay for community policing initiatives
- Body cameras and storage systems
- Emergency response equipment
- Professional development and training
Even within these categories, adherence to guidelines is critical, as restrictions often apply.
On the flip side, unallowable costs are explicitly prohibited by federal regulations or fail to meet the allowability criteria. These include:
- Entertainment expenses
- Alcoholic beverages
- Lobbying activities
- Purchases unrelated to the grant’s purpose
Every expense must be backed by documentation proving it is reasonable, necessary, and directly tied to the grant. This means keeping detailed records like timesheets for personnel costs, receipts for equipment purchases, and clear justifications for any questionable expenses.
Indirect costs, such as utilities or administrative salaries, present unique challenges. Federal grants permit indirect costs, but only at approved rates through a formal indirect cost rate proposal or the de minimis rate of 10% of modified total direct costs. These guidelines set the stage for procurement and monitoring requirements.
Procurement Standards and Documentation
Federal procurement rules are designed to ensure grant funds are spent effectively and equitably. The standards become stricter as the purchase amount increases.
- Micro-purchases (under $10,000): Require evidence of reasonable pricing, such as informal quotes or online price checks.
- Purchases between $10,000 and $250,000: Require price quotes from at least three qualified sources, when feasible.
- Formal procurements (over $250,000): Demand public advertising, sealed bids or competitive proposals, and detailed evaluation criteria.
Agencies must also implement conflict of interest policies. Employees, officers, or agents involved in procurement cannot have financial interests in the outcome, including situations benefiting family members.
The Buy American Act mandates that equipment purchased with federal funds must be American-made unless specific exceptions apply.
Documentation is critical at every step and must include the procurement method used, the rationale for contractor selection, and justification for sole-source purchases. Sole-source procurements are permitted but require written explanations showing the item is only available from one source or that competition is not feasible.
Subrecipient Monitoring
When federal funds are passed to partner organizations, the responsibility for compliance doesn’t end - it expands. Agencies must monitor these partners, known as subrecipients, to ensure they meet federal requirements.
First, determine if your partner is a subrecipient (responsible for carrying out part of the program) or a contractor (provides goods or services). Subrecipients must adhere to the same federal rules as your agency.
Effective monitoring begins with risk assessments, evaluating each subrecipient’s experience with federal programs, financial stability, management systems, and audit history. Higher-risk subrecipients require more intensive oversight.
Key steps in subrecipient monitoring include:
- Providing clear award documentation outlining federal requirements, compliance obligations, and any additional conditions based on risk.
- Conducting ongoing monitoring, which could involve reviewing financial reports, site visits, and offering technical assistance. High-risk subrecipients may require more frequent reporting or additional oversight.
- Ensuring compliance with the Single Audit Act for subrecipients spending $750,000 or more in federal awards annually. This includes verifying audits are completed and addressing any findings related to your grant.
By maintaining rigorous oversight, agencies can ensure their partners meet compliance standards, complementing their internal controls.
Audit Thresholds and Reporting Obligations
Clear audit and reporting processes are vital for maintaining compliance. Federal audit requirements depend on the total federal funding an organization receives.
Organizations spending $750,000 or more in federal funds during a fiscal year must comply with Single Audit requirements. This includes all federal funding sources, such as grants, contracts, and loan guarantees. Organizations below this threshold are exempt but must still maintain records for federal review.
Financial reporting obligations include submitting Federal Financial Reports (FFR) quarterly or annually. These reports reconcile expenditures by cost category with accounting records.
Performance reporting measures progress toward grant objectives. This involves submitting annual reports with quantitative data on outputs and outcomes, along with narrative descriptions of activities and challenges.
Agencies must also be prepared for special reporting situations. For example, significant events like changes in personnel, cost overruns, or project delays often require notification within 30 days, along with corrective action plans.
If subject to Single Audit requirements, agencies must submit a Data Collection Form (SF-SAC) within nine months of their fiscal year-end. This form summarizes audit findings and corrective actions.
Finally, record retention requirements mandate that records be kept for at least three years after final expenditure reports are submitted. Some programs may require longer retention periods. These records must remain accessible for federal review and audits to protect funding eligibility.
Preparing for Audits and Mitigating Compliance Risks
When it comes to compliance requirements, staying prepared for audits is more than just a safeguard - it's a way to protect current funding and keep future opportunities within reach. Agencies, especially those in law enforcement and municipal sectors, benefit greatly from maintaining strong documentation practices. These practices not only simplify the audit process but also minimize the risk of compliance violations.
Audit Preparation Checklist
Getting ready for an audit starts with understanding what auditors will focus on. For federal grant audits, this means an independent review of how your organization has managed and spent its funding. Auditors will verify that the funds were used in line with the grant’s specific conditions [1]. This process often involves a detailed review of financial statements, accounting records, and supporting documents like receipts and contracts [1].
Here are the key areas to focus on:
- Financial Documentation: Keep detailed financial records, including invoices, receipts, timesheets, and bank statements. If your funding spans multiple grants or tax years, ensure each cost is clearly separated [1]. This level of organization avoids confusion and demonstrates attention to detail.
- Grant Agreement Review: Before the audit, revisit the grant agreement to confirm eligible and ineligible costs, reporting deadlines, and other conditions. Catching potential issues before auditors do can save your agency from unnecessary headaches.
- Staff Preparation: Auditors may interview key personnel, such as project managers and finance officers, to assess internal controls [1]. Make sure your team understands their responsibilities within the grant program and can confidently explain their processes.
- Record Organization: Consistently organize and back up digital records. Use clear naming conventions and create separate folders for financial records, correspondence, reports, and supporting documents for each grant.
Even with these measures in place, agencies often encounter common compliance challenges.
Common Compliance Pitfalls
Many compliance issues can be avoided with proper planning and oversight. Here are some frequent pitfalls and how they can impact your agency:
- Poor Documentation Practices: Insufficient documentation for expenses is a major compliance issue. Missing receipts, incomplete timesheets, or vague descriptions that fail to link costs to grant objectives can create significant problems during audits.
- Inadequate Expense Tracking: Delaying the logging of expenses can lead to incomplete or inaccurate records. Establishing a system to record expenses as they occur ensures smoother audits and reduces the risk of discrepancies [1].
- Mixing Grant Funds: Combining funds from different grants without clear separation can cause confusion, especially for agencies managing multiple federal grants. Each grant has its own requirements, and failing to track expenses separately can lead to compliance violations.
Using Internal Controls to Reduce Risk
Strong internal controls act as a safety net, helping agencies avoid compliance issues by creating systems of checks and balances. Here’s how these controls can make a difference:
- Segregation of Duties: Assign different roles for approving expenses and processing payments. This division reduces the risk of errors or fraud by building natural checkpoints into the process.
- Approval Workflows: Define clear authorization levels for expenses. Written policies should specify who can approve certain amounts and what documentation is required, ensuring all expenses are verified as allowable and reasonable before payment.
- Regular Reconciliation Processes: Perform monthly reconciliations to compare grant budgets with actual expenditures. This practice helps catch errors early and ensures spending stays within approved limits. Use variance analysis to explain any major differences.
- Regular Risk Evaluations: From the moment a grant is awarded to the final reporting stage, evaluate risks like personnel changes, budget modifications, or timeline shifts. Document strategies to address these risks and keep your agency prepared.
- Training Programs: Keep staff up-to-date with ongoing training on regulations and grant conditions [1]. Well-trained teams are better equipped to identify and address compliance challenges as they arise.
sbb-itb-6e14cfc
Key Updates to Federal Grant Regulations in 2025
Federal grant regulations evolve frequently, and the 2025 updates bring changes that law enforcement and municipal agencies must address to stay compliant. These adjustments touch on several aspects of grant management and require immediate attention.
Major Revisions in Uniform Guidance
The 2025 updates to the Uniform Guidance focus on several critical areas: audit thresholds, cost allocation methods, cybersecurity protocols, and subrecipient monitoring. These changes are designed to refine compliance processes and improve oversight. Agencies should carefully review the official guidance to understand how these updates affect their grant management practices and make necessary adjustments without delay.
Impact on Grant Management Policies
To remain compliant, agencies need to revisit and revise their internal policies. Key areas to examine include procurement practices, financial management systems, reporting schedules, and protocols for handling sensitive information. Ensuring these processes align with the updated federal standards is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding potential penalties.
Steps to Meet New Requirements
- Review and update policies: Compare existing grant management policies with the new federal guidelines to identify gaps.
- Train staff: Update training programs to educate team members about the latest compliance requirements.
- Strengthen documentation and controls: Refine internal controls and improve record-keeping to meet the revised standards.
- Upgrade technology: Implement necessary enhancements to cybersecurity measures and financial management systems.
- Monitor compliance regularly: Establish routine checks to ensure ongoing adherence to the updated regulations.
Grantwell's Role in Federal Grant Compliance
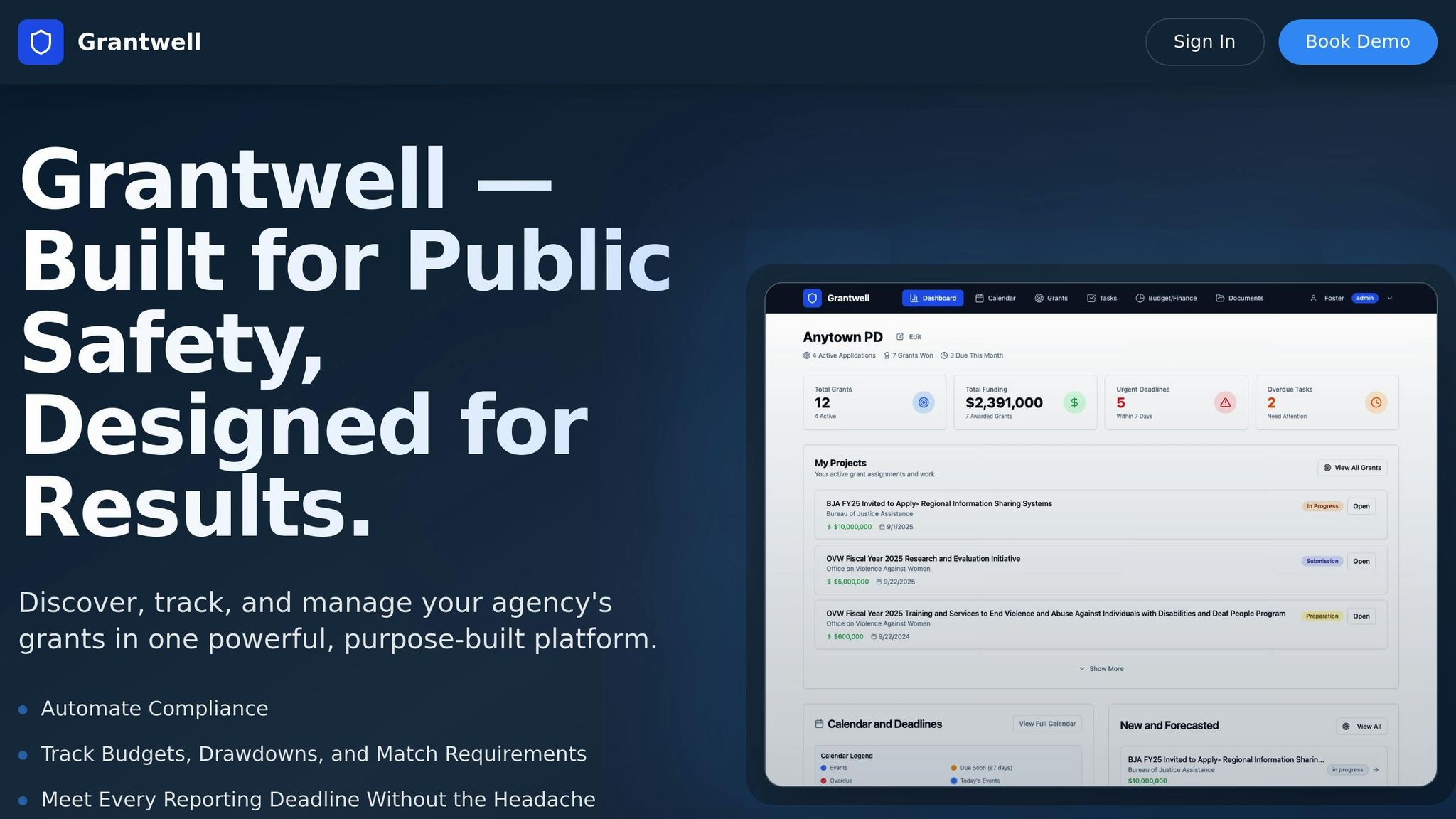
Navigating federal grant compliance can be a daunting task, but a well-designed technology platform can make it much easier. Grantwell is a grant management system tailored specifically for law enforcement and municipal agencies, aligning with CJIS and FedRAMP standards. By turning complicated federal compliance requirements into automated processes, it helps reduce administrative workload while ensuring all regulations are met. Let’s dive into how its features simplify compliance.
Automated Compliance Features
Grantwell offers a suite of automated tools that make staying compliant far less stressful. Tools like the budget vs. actual tracker, smart alerts, real-time drawdown calculations, and an integrated budget builder help agencies stay in control of their grant spending. These tools monitor expenditures, provide timely alerts, and allow for budget adjustments that align with federal standards. With real-time tracking and automated notifications, agencies can stay within grant limits and meet deadlines without scrambling. Plus, these features set the stage for smoother audit preparation.
Simplified Audit Preparation
Preparing for audits can feel overwhelming, but Grantwell makes it easier by continuously tracking expenditures throughout the grant's lifecycle. The platform’s expense pipeline management and compatibility with JustGrants allow agencies to generate ready-to-use CSV exports for audit reviews. This ensures that all necessary documentation is organized and accessible when needed.
Tailored for Municipal Agencies
Grantwell is particularly beneficial for public safety and law enforcement agencies. It includes features like subrecipient risk tracking and match contribution monitoring, which help ensure that all partners and local funding commitments meet federal regulations. The platform also automates final reports, speeding up the grant closeout process. Additionally, it’s built to handle multiple funding sources, keeping compliance for each grant separate. This is especially helpful for managing the varied requirements and reporting schedules of federal programs.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Federal grant compliance doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By focusing on clear strategies and leveraging the right tools, you can confidently navigate the complex requirements. Key areas like allowable costs, procurement standards, subrecipient monitoring, and audit preparation form the backbone of a solid compliance framework. The best approach? Stay ahead of the curve rather than reacting to issues as they arise.
Compliance Requirements Summary
To recap, successful compliance hinges on a few critical practices: clear cost segregation, thorough procurement documentation, and robust internal controls. These measures not only mitigate risks but also ensure smoother operations.
Audit preparation, for example, should be an ongoing effort, not a last-minute rush. If your federal funding reaches the Single Audit threshold of $750,000, you’ll face comprehensive audit requirements. Even if you don’t meet that threshold, maintaining year-round audit-ready practices is invaluable. This includes keeping detailed records of expenses, consistently comparing budgets to actual spending, and documenting every procurement decision.
The 2025 updates to Uniform Guidance have added new layers of complexity, such as stricter reporting timelines and more rigorous subrecipient monitoring. To stay compliant, organizations need to adapt their internal processes to meet these updated standards while continuing to align with existing regulations.
How Grantwell Supports Compliance Goals
Grantwell simplifies compliance by automating key tasks, making it a powerful ally for law enforcement and municipal agencies. Its real-time budget tracking, automated alerts, and integrated audit preparation tools significantly reduce the manual workload tied to compliance.
One standout feature is its expense pipeline management, which ensures that every expenditure is categorized and documented from the start. This continuous tracking system transforms audit preparation into a straightforward process of generating reports, rather than a frantic search for financial records. Plus, the platform’s compatibility with JustGrants and its ability to create clean CSV exports streamline reporting even further.
For agencies juggling multiple federal grants, Grantwell’s ability to keep compliance tracking separate for each funding source is a game-changer. This prevents overlapping requirements and ensures that every grant’s specific obligations are met without confusion.
With tools like these, achieving compliance becomes not just manageable but efficient.
Take Action
Now’s the time to take control of your federal grant compliance. Start by evaluating your current processes with our checklist to uncover any gaps or risks in your documentation and tracking methods.
Consider scheduling a demo with Grantwell to see how its automated features can tackle your unique compliance challenges. Designed with the needs of law enforcement and public safety organizations in mind, Grantwell offers a streamlined approach to managing federal grants.
Don’t wait - improving your compliance processes today means fewer audit findings and quicker grant closeouts tomorrow. Take the first step toward a more efficient and stress-free compliance journey.
FAQs
What are the key federal grant compliance updates for 2025, and how might they impact my organization?
Several updates to federal grant compliance regulations are set to roll out in 2025, bringing changes that could reshape how organizations handle their grants.
Here’s a quick rundown of the key updates:
- Executive Order 14332: Federal agencies are now required to appoint senior officials to oversee grantmaking activities, ensuring these align with national priorities.
- Uniform Guidance Updates: New provisions allow federal awards to be terminated “for convenience” and impose stricter limits on the use of funds for indirect costs.
- HHS Grants Policy Statement (GPS): Updated policies will apply to both new and active awards, fully integrating 2 CFR Part 200 by October 1, 2025.
- Increased Thresholds: Higher limits have been set for subawards, equipment, supplies, and single audits.
These changes signal a push for tighter oversight, stricter eligibility requirements, and more detailed scrutiny of grant applications. Organizations should revisit their compliance strategies to ensure they’re ready to demonstrate how their programs align with federal priorities.
What steps should my agency take to monitor subrecipients and ensure compliance with federal grant rules?
To help subrecipients meet federal grant requirements, it’s important to adopt a well-organized and forward-thinking strategy. Begin by clearly outlining the terms of the subaward. This should include all relevant federal statutes and specific award conditions. Regularly require both programmatic and financial reports to confirm that everything aligns with compliance standards.
Assess the risk of noncompliance for each subrecipient to tailor your monitoring efforts. This might involve reviewing their audit results, addressing any identified issues, and offering training or technical support to close any gaps. Consistent communication and thorough documentation of oversight activities are critical to ensuring accountability and minimizing the chances of noncompliance.
What are some common mistakes organizations make with federal grant compliance, and how can we avoid them?
Organizations frequently struggle with federal grant compliance for a variety of reasons, including weak financial management, poorly maintained records, misuse of funds, and non-compliance with grant regulations. These missteps can result in serious consequences like fines, revoked funding, or even disqualification from future opportunities.
To steer clear of these problems, it's crucial to put effective financial management systems in place, keep thorough and well-organized records, and ensure that every expense adheres to the grant's specific requirements. Adding strong internal controls to your processes is another essential step. Regular audits and ongoing staff training on compliance standards can further ensure your team remains aligned with federal guidelines.